The linen and laundry service is an important utility service which not only helps contain the hospital infections but also contributes to the image of the hospital. Clean and crisp linen has a very soothing and assuring effect on the patient’s psyche while dirty linen is bound to cause patients’ dissatisfaction and negative impressions about the entire hospital. It is, therefore, essential for every hospital to maintain high standards of linen and laundry service so as to ensure full satisfaction of clients, both external (patients/relatives) and internal (doctors/nurses/technicians).
Depending upon the policy, the hospital may have its own laundry service, outsource it or have their own facility run by a contractor on contractual basis. In any situation, the responsibility of quality of services lies with the hospital management.
Hospital linen can be classified as follows:
a. i. Hospital linen
ii. Body Linen
iii. OT Linen
b. Staff Linen
c. Linen for housekeeping of offices like curtains etc. for departments and wards
2. Laundry Linen
a.Infected Linen
b. Soiled Linen
c. Foul Linen
d. Radioactive Linen
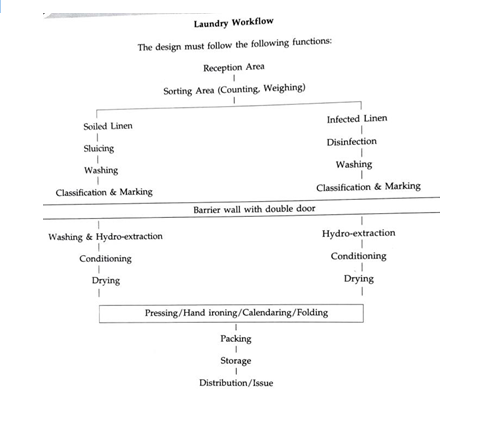
Counting and sorting soiled linen by processing type:
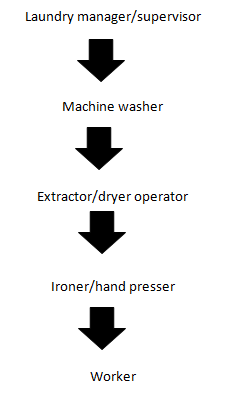
In many hospitals, laundry is attached to the house keeping department or CSSD. In large hospitals, it functions independently.
Fouled or infected linen and normally soiled linen should be separately handled and washed. This area should be separated from the rest of the reception area and from the post wash clean area of the laundry. The infection control unit should focus its attention on laundry services at par with CSSD to ensure infection control measures are observed meticulously.
The various types of laundry services can be classified as under:
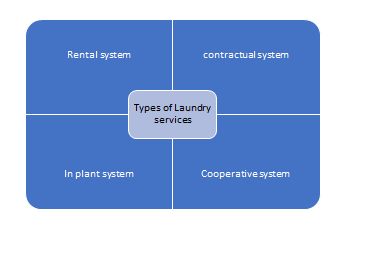
3. In plant system: The hospitals have their own laundry plant. It is one of the best methods for hospital laundry, but sometimes the operating cost is the limiting factor. This type of laundry is more suitable for hospital of big size.
4. Cooperative system: A group of hospitals may utilize the laundry services of one plant on cooperative basis. It is suitable for hospital of small size or nursing homes. The disadvantage of mixing of the hospital linen and cross infection is inherent.
The following systems are prevalent:
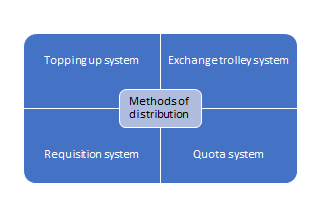
3. Requisition system: This is based upon the indenting system. A written requirement is submitted to the central linen supply department and on the basis of requisition the linen is supplied to the demanding units as on when required basis.
4. Quota system: It is usually a daily quota system, there is predetermined, prefixed requirement for each unit, the linen is supplied directly from the central linen store. The only disadvantage in this system is; if the imprest has not been determined realistically, the linen may accumulate at the user units.
The requirement of the linen is calculated on the basis of actual performance of the user units like:
As a rough guide 2 to 3.5 kg of dry linen per patient per day is required. If we presume bed occupancy rate is 100% six sets of linen are required as:
It is conveniently located in the ground floor. It should be closer to the user units. Close proximity to CSSD and Dietary services is desirable, due to common requirement of steam from boiler plant.
Space Requirement: The space requirement is 10 sq. feet/bed.
Physical Layout: It depends upon work flow; it can be “U” shaped or rectangular type.
The following ancillary facilities are requisites of the laundry services:
10 air changes per hour are the recommended air changes for proper ventilation.
There should be three phase connections. The distribution panel should be easily accessible. There should be stand by generator. For motorized equipment’s 3 kW hour per 45 kg of dry laundry and for laundering, it is recommended as 3 Watts per 1/ 3 sq. meter of floor area.
There should be provision of adequate supply of water. Approximately 15 litre of hot water and 10 litres of cold water are required per 0.5 kg of linen processed. If there is supply of hard water then softening of water is done with the help of softening plants.
The steam supply system must deliver steam to the equipment’s at the required temperature. A temperature of 170°C is obtained from steam at 45 kg per 6 sq. cm pressure. All steam lines should be properly insulated for protection of the workers.
There should be provision of fire detection system with alarm and system of fire extinguishing in place, to prevent fire hazards.
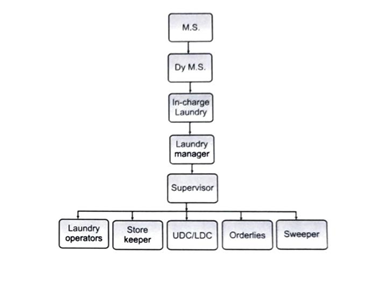
The hospital laundry must have a well-trained laundry manager as he has to supervise the work of very technical nature and at the same time, most of the work is carried out by the non-technical personnel like Dhobis who do not know the importance of hospital infection control.
| S. No. | Staff | Number |
| 1 | Laundry manger | 1 |
| 2 | Laundry supervisor | 1 |
| 3 | Store keeper | 2 |
| 4 | Orderlies | 6 |
| 5 | Tailors | 1 |
| 6 | Safaiwala | 1 |
| 7 | Operators | 17 |
As a rough guide 1 man per 30 beds in hospital. As per the recommendation of U.S. Department of health, approximate number of personnel required as:
| Types of linen | |||
| Cleaning Agent | Cotton white 100-pound dry weight | Cotton white 100-pound dry weight | Woollen pounds weight |
| Washing soap | 1.5 | 1 | 1.5 |
| Washing soda | 1 | 0.5 | – |
| Bleaching powder | 0.5 | – | – |
| Whitener | 0.05 | – | – |
| Starch | – | 1 | – |
| Temp. | 140 – 160 °F | 150 °F | 60 °F |
The laundry service in hospital is heavily depended upon the equipment’s. Every day some new equipment is being added to the list or some up gradation of equipment is being done. There is need of judicious equipment procurement planning and above that preventive planned maintenance program of the equipment. The number and types of the equipment’s will depend upon various factors. The important one are:
Some of the equipment’s are being enlisted as follows:
The contaminated laundry can be defined as “laundry which has been soiled with blood or other potentially infectious material or may contain sharps.” Potential hazards: Exposure to blood or other potentially infectious materials through contaminated laundry that was improperly labelled, or handled.
a. Potential Handling: Exposure to blood borne pathogens from contaminated laundry; that contains sharps.
b.Possible solutions: A safety and health program that includes procedures for appropriate disposal and handling of sharps and follows required practices outlined in the Blood borne Pathogens Standard.
c.Contaminated needles and sharps: Shall not be bent, recapped or removed. No shearing or breaking permitted.
d. Sharps Containerization: Immediately or as soon as feasible. Contaminated sharps need to be discarded in appropriate containers. Needle containers need to be available, and in close proximity to areas where needles may be found, including laundries.
10. Ergonomics
11. Quality assurance in laundry
12. Staffing functions: Clarity in roles and responsibility among the supervisors and staff, training of staff, schedule of working hours, occupational safety measures for staff.
13. Physical facilities and plant: Location of laundry. In relation to boiler room, source of hot water, steam, electric supply, noise control, ventilation, lighting, and vibrations. 13. Linen handling: System of handling of dirty, soiled, infected and contaminated laundry. System of control of accounting of linen sent to laundry and when it leaves the laundry.
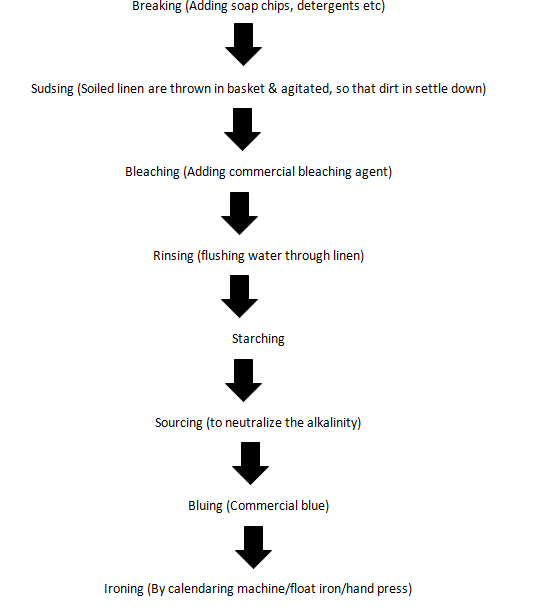
14. Laundering process: Sorting, segregating, washing formula, steps taken to remove stains, laundering process of special linen, control of damaged linen etc.
15. Linen control: Linen control program through linen control committee. Right from the procurement procedure to the final disposal, that is inventory control of the linen. The students are advised to consult chapter on material management in the same book and to go into the details of inventory control techniques.
16. Sewing room: Location of sewing room, items to be stitched, sewing machines in use, marking method of new linen.
17 . Cost: The total cost of laundry, distribution of laundering costs to various user units, the factors determining the cost of the laundering, the present valuation of laundry, the depreciation costs of various equipment’s installed in the laundry.
18. Quality assurance program: Through quality circles and by application of “5 S” technique of sorting, segregating, shine, standardize and control. These 5 ‘S’ have been derived from Japanese literature, as this technique of control is very popular in Japan.
19. Hospital infection control: Contaminated linen must be disinfected before issuing to dhobis. Both contaminated and clean contaminated should be transported to laundry, separately. Handling, separating, and counting of even clean contaminated linen is hazardous, hence there should be minimum handling. Drying of linen in the sun after washing should be discouraged as it usually spreads on road side or other contaminated area, poses risk to the general public.
a. Decontamination of blankets: Cotton and acrylic blankets are preferred to woollen blankets. They can be handled like linen; contaminated soiled woollen blankets can be decontaminated either by exposing to formaldehyde vapours or autoclaving. Liquid disinfectants may damage woollen blankets. The woollen blankets can be dry-cleaned but it does not inactivate HIV/ AIDS.
b. Decontamination of mattress: It is advisable to cover all mattresses with water proof synthetic material like raxine or plastic. Big autoclaves are available for disinfection of mattresses. Washing can be done manually.
a. The timeliness of linen supply
b. The quality of linen supplied (worn out/faded, stained, patched, smelling or poorly ironed)
c. The quantity of linen supplied
3. Average monthly cost of linen replacement
4. Losses due to thefts, pilferage or damage in process.
Linen service in a hospital plays an important role in providing an infection free, clean and fresh environment to the patients. Unclean, stained, patched and smelly linen, like bad quality food, can be a major source of dissatisfaction of the patients. It conveys a poor impression about the entire hospital. Not only that, it adds to the chances of cross infection. A good, patient focused service must eliminate all such deficiencies. High quality linen and laundry services, however, require a well planned mechanized laundry with adequate supply of the right quality water and consumables as well as adequate and well trained staff. It also requires a sustained effort at process control and improvement through standardized procedures covering all the activities, as a part of a continuous program of quality management.