In spite of all the remarkable advancements in medical science, hospital-acquired infection remains a serious problem in health care today. To make every effort to overcome this, hospitals must have a scientific and effective method of disinfection and sterilization called central sterile supply department (CSSD).
The central sterile supply department is responsible for providing sterile supplies of surgical Instruments, equipment, linen, and clothing. It serves the nursing units, operating rooms, intensive care units, delivery suites, nursery, outpatient department, accident and emergency, radiology, and clinical laboratories. The primary activities of the department are sterilizing, storing and distributing the dressings, needles and syringes, rubber goods (gloves, catheters, tubing), instruments, treatment trays and sets, linen packs, etc. There is one exception to the range of materials that should be sterilized centrally: the surgeon’s instruments used in major operating theatres. Because so many surgeons like to have their own individual sets of adjoining instruments, it is generally more convenient to arrange for these to be sterilized in a room the operating room. All other requirements for operations, including dressings, bowels, syringe, and so forth, can be supplied to the operating room from the CSSD.
CSSD is a service unit in a hospital that processes, issues, and controls the sterile stores supply to all departments of the hospital.
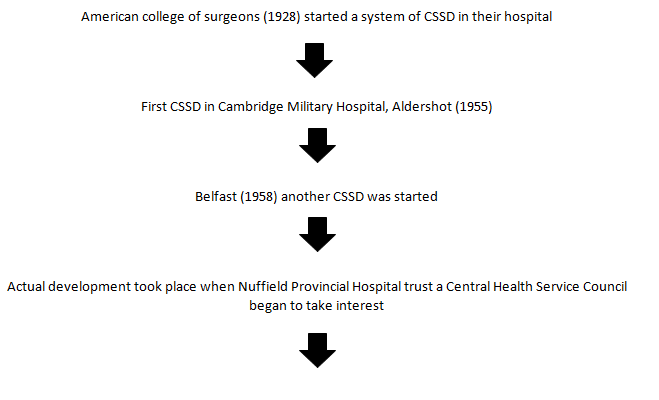
Now, CSSD in an integral part of every hospital
To provide the safe and sterile supplies to all the user units of the hospital.
To sterilize and supply
All storage areas should be clean and protected from condensation and vermin. Store cupboards should be warm and adequately ventilated. Work involves the possibility of workers sustaining cuts from instruments and burns from sterilizing equipment. Much of the work is repetitious.
Usually, attached to the nursing department, a senior nursing staff, dedicated and hard working is sent for training for sterilization of hospital equipment’s and later the same person will be posted as the in charge of the department under the supervision of the nursing matron
Apart from the in charge two or three in-service trained CSSD technicians will be posted. Whereas in the big hospitals, a separate CSSD department with qualified personnel with modern equipment’s will be maintained.
Quality management of services in CSSD is extremely important in view of its role in the hospital infection control and the catastrophic effects the poor-quality services may have on the patients. However, quality of services can best be judged from level of satisfaction of the clientele. The clients in case of CSSD are all internal (consumer departments/clinicians) and high quality CSSD services to them means:
The following departments and its items to be supplied properly on time without any hindrance
Diagnostic equipment
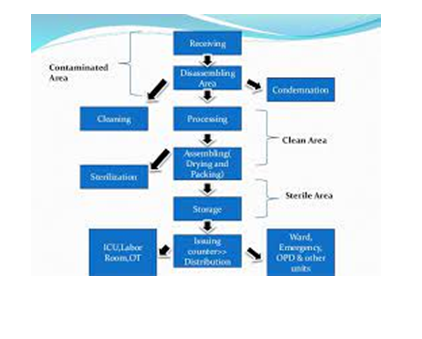
It should be ideally located in close proximity to the user units, i.e., OT, ICU, Wards, Emergency and Labour room for effectiveness and efficiency. It should have adequate facility of cold and hot water, steam and compressed air and electricity.
The minimum area in square feet required per bed as recommended (Giford, DL-1963).
| No of Beds | Space Requirement |
| 75-99 beds | 10sq. feet/bed |
| 100-149 beds | 9sq. feet/bed |
| 150-200 beds | 8.5sq. feet/bed |
| 200-249 beds | 8sq. feet/bed |
| 250-299 beds | 7.5sq. feet/bed |
| More than 300 beds | 7sq. feet/bed |
As a rule of thumb, the following requirement of CSSD in hospital
| S. No | No of Hospital beds | Type of facility |
| 1 | Hospital up to 100 beds | TSSU |
| 2 | More than 100 beds | CSSD in service area |
| 3 | More than 500 beds | CSSD in service area and TSSU in OT |
The total space is functionally divided into the following areas:
The flow of work should be unidirectional and without back tracking to prevent mixing of sterile goods with the unsterile goods.
The CSSD staff will include:
The staff strength varies from hospital to hospital depending upon the bed strength and work load as a rough guide hospital management (1961) has recommended one employee per 30 beds.
The types of equipment’s required in the CSSD are:

“Ethylene oxide sterilizer” is defined as equipment which uses ethylene oxide as a biocide to destroy bacteria, viruses, fungus and other unwanted organisms. Ethylene oxide is used in sterilization of items that are heat and moisture sensitive. Ethylene Oxide (ETO) is a chemical agent that kills micro organisms by stopping the normal metabolisms of protein and reproductive process resulting in death of microorganisms. This is a commonly used sterilizer in various industries including Medical-Disposable equipment suppliers, pharmaceuticals, museums, and hospitals.
Steam sterilization is most commonly used sterilization because it is safe, inexpensive, and time saving. The outer layer of some microorganisms is softened by the steam which coagulates the internal portion of the organism. In this way, steam sterilization is effective against microorganisms. The steam sterilizer is operated either by supply of steam passed through a pressure reducing value from the boiler or by in built electrical steam generators. Steam sterilizers are used for sterilization of glass wares / containers, vessels, linen, rubber articles, operation theatre instruments, etc.

Dry Heat Sterilizer is effective mode of sterilization. It is an equipment with electric resistors distributed inside the cabinet that is isolated with a panel for temperature control. Dry heat will penetrate all kinds of materials, such as oils, and closed containers.
Dry Heat Sterilizer is used to do dry sterilization of surgical instruments, medical, dental, aesthetic, laboratories, industries and other glassware’s.

Sterilization process needs high quality pure steam with accurate pressure control. The steam generator removes non-condensable gases.

An efficient aid for the cleaning and the thermal disinfection of all Medical, Dental and Laboratory instruments. A washer of a modern concept, designed and constructed in compliance with the guidelines indicated in the new European Norm concerning safety and hygiene. The washer can be placed on any work surface and is simple to install, the built-in detergent compartment and dispenser are standard features.

Sterilization is a process of freeing an article from all living organisms including bacteria, viruses, fungi and spores. The sterilization process prevalent in hospitals can be classified as:
a. Dry heat sterilization
b. Sterilization by steam
2. Ethylene Oxide Gas (ETO) Sterilization
3. Chemical sterilization
4. Radiation sterilization- Gamma radiation
a. Heat sterilization by dry heat: In the conventional hot air oven, the sterilization is carried out at about 160°C for 1 hour. The most suitable article for dry heat sterilization is glass wares, particularly glass syringes, but now the use of glass syringes has become almost obsolete. Another article is cutting edge instrument.
b. Heat Sterilization by Steam: The item are first of all prepared for steam sterilization in the following manner:
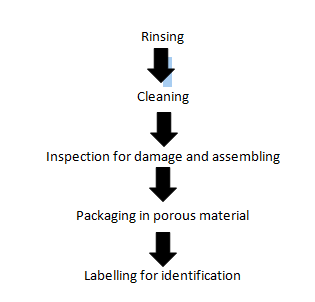
Each type of the item is subjected to temperature of 134°C for 3 minutes on 121°C for 15 minutes. Flash sterilization or quick sterilization technique is usually preferred in TSSU, because flash sterilizer achieves a temperature and pressure for sterilization in minutes.
a. Disinfectant: Applied to inanimate objects. Ii. Antiseptic: Applied to living tissue (anti sepsis).
b. Degerming: Mechanical removal of most microbes in a limited area, e.g. Alcohol swab on skin.
c. Sanitization: Use of chemical agent on food handling equipment to meet public health standards and minimize chances of disease transmission, e.g. Hot soap and water.
| Process | Agent Used | Status |
| Disinfection Sterilization | Orthophtaldehyde (Cidex) | FDA cleared 1999 |
| Antimicrobial coating (Surfacing ) | Not cleared by FDA | |
| Superoxide water (sterilox) | Not cleared by FDA | |
| Liquid sterilisation | Not cleared by FDA | |
| Rapid read out ethylene | ||
| Oxide biological indicator (Attest) | Not cleared by FDA | |
| New Plasma sterilizer (sterrad) |
New Disinfectant (Superoxide water): Concept of electrolyzing to create a disinfectant (saline +electricity) Sterilex (mixture of oxidizing species). Main products Hypocholorous acid (144mg/1) and chlorine radicals. Passing saline soln. over titanium coated electrode. Super oxidized water is rapidly effective (<2 min) reduce 5-log 10. Effective against Mycobacteria, viruses, fungi and spores. But organic material may reduce its effectiveness.
Chemical Sterilization System (Endocleans): Chemical use in endoscope-reprocessing system/machine controlled by computer. Chemical Sterilant that uses Performic acid generated by Hydrogen peroxide and formic acid. Effective against wide range of Bacteria and spore (less than 30 min). In whole process, two endoscope simultaneously can be cleaned. Washing, rinse detergent, cleaning, enzymatic detergent, leak detection everything can be performed.
Chemical methods of microbial control: Halogens: Effective alone or in compounds.
When mixed in water forms Hypocholorous acid:
Cl₂ + H₂O → H+ + Cl– + HOCI
(Hypocholorous acid)
Used to disinfect drinking water, pools, and sewage.
Chlorine is easily inactivated by organic materials.
This area receives all the sterilized items from the sterilization-processing unit. Items are classified and separated again department wise to reassembling the set to ready for reuse. As a set it is ready for packing to supply the sterilized items to the concern departmental use.
Periodic and regular monitoring of infections occurrence or presence of patient, operation theatre, intensive care unit, accident and emergency service, wards, etc. within the hospital by patient blood sample investigation and report on swab culture of the section or equipment or instruments with the help of microbiologist. If any infectious case is found and it should be reported immediately hospital administration, infection control committee, and alert the concerned those who are involving particular patient or section. Also, the proper policies and procedures of infection control should be
6.Labelling: Labelling is done for identification and for knowing shelf life of item. Following details must be noted while labelling:
a. Identification number.
b. Barcode: If bar code facility is existing
c. Contents of pack
d. Date of sterilization
e. Shelf life
f. Quality check certificate “OK”
g. Initials of person who carried out sterilization
h. Initial of quality control person
i. Initial of packer
7. Sterilization: As per requirement, type of the article and as per the standard procedures.
8. Storage: There should be a separate storage area for sterile and unsterile goods.
9. Distribution: To provide quality medical care, there should be an effective distribution system. There are following types of distribution system in practice:
a. Topping up: The predetermined levels of each item are fixed for each user unit. Maintaining these items at fixed levels. Topping up round are taken from CSSD.
b. Clean for dirty exchange: One clean article for each dirty returned to the CSSD by user unit.
c. Ordinary order system: The materials which are required by the user department are ordered directly to the CSSD as and when required basis.
d. Regular Complete stock Issue: Complete requirements of the user units are determined and full box, trolley or basket containing all such items. Are issued to the user units. At a regular interval, the full quota is replaced by the CSSD, whether the part or full quantity has been utilized by the user unit or not. Meaning thereby full quota is exchanged between user unit and CSSD.
There should be a well documented policy of the CSSD and procedure manuals for all the procedures to be carried out in the CSSD, should be in place and be followed correctly:
a. Ensure proper sterilization procedures carried out in the CSSD.
b. Ensure safe storage, adequate in proper packing and labelling of sterilized items for the respective departments.
The biological indicators have been used worldwide by medical and industrial facilities to monitor steam, d low temperature steam, formaldehyde, ethylene oxide gas, propylene oxide gas, dry heat, hydrogen r peroxide, and radiation sterilization processes. The Smart-Read system includes the Smart-Read EZTest self-contained biological indicator for steam which is specially designed for rapid evaluation in the advanced Smart-Well® incubator.
The Smart-Read TM EZTest® Biological Monitoring System allows an organization to release sterile product with true biological confirmation faster and easier than ever before. This unique system uses a real biological indicator (BI)-with no added enzyme or chemical integrator-which is incubated, evaluated, and documented in one simple, automated operation. Relying only upon bacterial spore growth, the Smart-Read system can detect sterilization failure in as few as 3 to 5 hours, and confirm sterilization in only 10 hours. The Smart-Read system includes the Smart-Read EZTest self contained biological indicator which is specially designed for rapid evaluation in advanced Smart Well incubator. Based on familiar, proven technology, the Smart-Read system can be implemented by any organization with minimal training and validation.
Though a highly sophisticated tool, the Smart-Well incubator is easy to configure and monitor with its simple touch-screen interface. The incubator can evaluate up to ten Smart-Read EZ Test biological indicators independently, and contains an additional cell for a positive control unit. Each BI test result is automatically documented with a user-customizable printed report, and an alarm is sounded the moment that sterilization failure is detected. The incubator also contains an NIST-traceable thermometer marked at the appropriate incubation temperature to allow the operator to quickly verify proper operation.
The Smart-Well incubator is offered in a kit including the incubator itself, stylus, report printer, record book for storing reports, thermometer, and all necessary cabling.
CSSD is a very important department from the quality point of view because quality and efficiency of this department can affect the quality of services of all other departments that use sterile supplies from CSSD. Therefore, the department should have adequate infrastructure of the right quality, including well trained manpower, facilities and equipment conducive to high level of asepsis. There should be documented policies and working protocols that are strictly implemented to ensure that sterilization procedures are carried out as per acceptable norms and standards. Not only that, there should also be a system of monitoring the quality of process as well as outcome so that deficiencies can be detected and timely corrective actions taken to prevent disquality.