Mortuary is a building or room in a hospital used for the storage of human remains. Morgue is predominantly used in North American English, whilst mortuary is more common in British English. The term mortuary or morgue is usually not mentioned in front of the patients in the hospitals, the euphemism “Rose Cottage is widely used in British hospitals to enable discussion in front of patients, relatives and visitors without disturbing them. In India, every hospital does not have mortuary. The mortuary is either available at the government run hospitals or with hospitals imparting teaching programs to undergraduates or postgraduates. There is social and medico-legal importance attached to the mortuary of the hospitals. Lot of sentimental values are attached with the dead body of the person. Therefore, the management of the mortuary is of significance for every hospital administrator.
There are two types of temperature-controlled chambers in mortuary.
The various functions of the mortuary services can be enumerated as follows:
One of the most important functions, of the mortuary services of the hospital is to preserve the dead body till it is finally disposed off. The types of the dead bodies coming to the mortuary can be classified as:
a. Identified
b. Unidentified
a. Identified
b. Unidentified
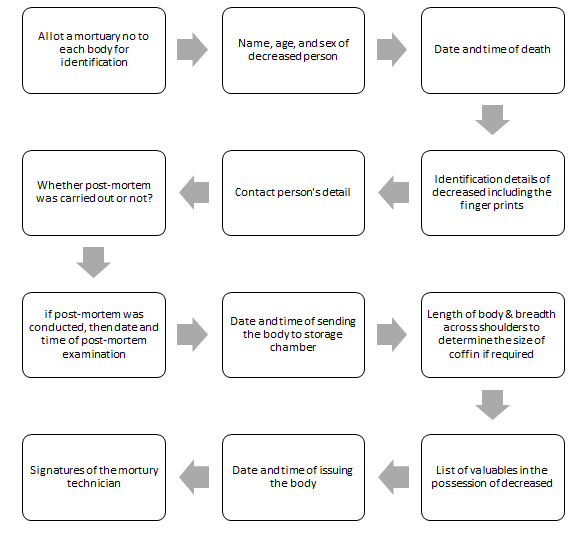
Documentation is an important activity of the mortuary service of the hospital. Every mortician munt If maintain a good quality ledger to enter all the details in respect of the bodies brought in to the mortuary. Preserved and disposed off by the mortuary. These records are to be maintained meticulously and all care must be taken to avoid over writing and cutting. If some entry is made incorrectly, or where corrections are to be made due to omissions, such entries must be attested try the authorised person with dated signature Following details are in respect of the dead bodies. there are facilities the database can be computerised It is easier to maintain and retrieve the data.
Relatives of the deceased are emotionally attached deeply even with the dead body and often, they want to transport the dead body to the place of their origin for funeral. For safe transportation of the dead body it is embalmed. Prior to embalming the following points need special consideration:
When someone dies and once authorization has been granted by the family, doctor, and/or by the medical examiner, the embalmer is called to make the “removal” of the body. After completing the formalities the embalmer takes the body to the funeral home, and begins the process.
An embalming report is prepared, which will include the, jewellery and personal items on the body; details of any discolorations, cuts, bruises, etc. on the body; and documents the procedures and chemicals used during embalming. The documentation becomes important evidence in support of the embalming process and this report can become very valuable if a deceased’s family bring a lawsuit against the funeral home. All clothing, bandages, IV needles, catheters are removed. A strong disinfectant spray is used to clean the skin, eyes, mouth, and other orifices. If rigor mortis, has set in, it is relieved by moving the limbs and head about and massaging the muscles.
The process of placing the facial features and the body itself in the position, it will remain in the casket for viewing. This is done before arterial embalming, because the body will be truly “set” firmed in position once formaldehyde reaches the tissues. The process of embalming is done as follows:
The most important part of the embalming process is the arterial injection of embalming fluids. Arterial embalming begins by selecting an artery to inject the fluid into and a vein to drain away blood. The C embalmer has a wide variety of embalming fluids available to him, Pre-injection chemicals break up clots and condition vessels. Co-injection chemicals restore dehydrated tissues, fight oedema, and correct hard water. The most important chemical, which is used for embalming is the arterial fluid, which is made up of preservatives, germicides, anticoagulants, dyes, and perfume. The main ingredient f arterial fluids C formaldehyde, but a few companies are manufacturing chemicals with less toxic properties like glutaraldehyde, but at the same time it is less effective also. The embalmer must inject about 1 gallon of fluid for every 50 pounds of body weight. A typical gallon of fluid might be made up of 1 bottle of arterial fluid, 1 bottle of co-injection fluid, 1 bottle of water corrective and sufficient water to complete the gallon.
The embalming fluid is injected with the help of embalming machines. The machine has got two knobs which regulate the pressure of the fluid being injected. The machine is switched on and the fluids begin to move through the hose, through the arterial tube and C into the body. Once the embalming fluid begins to flow into the vascular system, pressure begins to build up in the entire vascular system. This helps the fluid to reach all parts of the body and penetrate into the tissues. This is evident by the engorgement of the veins all over the body, which are usually collapsed – after the death. When the arterial injection has been completed, the arterial and jugular tubes are removed, the vessels are closed and the incision used to access the vessels is sutured and sealed with as special chemical.
The arterial fluids mainly treat the skin, muscles, and organs themselves. The organs begin to decompose. Cavity treatment starts with aspirating fluids out of the internal organs in the abdomen and thoracic cavity. The next process is of filling the cavities with the help of cavity fluids. It is very similar to arterial fluids, containing about the same percentage of formaldehyde. These steps apply only to body that has not been subjected to post-mortem examination, because during the process of post-mortem examination all the internal organs are removed and inspected by the medical examiner and then placed back inside the body are preserved and sent to chemical examiner and sometimes incinerated. If the viscera are not returned, then the empty cavity may be filled with adsorbent pads. In either case the autopsy opening is sutured closed and sealed.
Finger nails are trimmed. The hair is styled. The remains are dressed in the outfit chosen by the family. This outfit may include underwear, shoes; and socks. D In the case of autopsy, plastic undergarments are placed on the body to prevent leakage. The final process is of casketing; the body is placed into the casket and posed in a proper posture. The body is finally inspected by the family members and if any change is suggested, is done at this time. Now some cosmetic activity is performed, the body and hair are washed, if there is any blood stain on the body that is removed. Make up is applied to the body. The embalmer’s work will only be seen for a few days and then never seen again. However, for the family, the image they see of their loved one in the casket will stay with them forever. A poor job in the preparation room leaves the family with an undesirable memory. In the era of customer satisfaction great care is to be taken to satisfy the needs of the customer. For the embalmer it might be a dead body but for the family members it is still the loved one.
Location: it should be located in a separate building, near to the department of pathology, preferably in the ground floor or basement, having easy access from wards, emergency departments and operation theatres.
Size: There should be mortuary chamber for holding two bodies for a hospital of size 50-100 beds and at least of holding capacity of three bodies for a hospital of 200 beds.
Following physical facilities are desirable for a mortuary of large size of hospital or a hospital associated with medical college:
Space requirement will vary from hospital to hospital depending upon the size and type of hospital and also upon the work load and responsibilities of the mortuary services. Whether it is a part of forensic medicine or is a part of the forensic institute the space requirement will vary. Committee on Plan Project (COPP) has recommended an area of 6-8 sq. ft per bed as a general guide.
Floor
The floors should be of RCC, hard and durable, it should be easily washable and moisture proof and non-slippery.
Walls
The walls should be washable; preferably dadoing should be there; also, there should be scope for future expansion.
Windows
As far as possible, the natural day light should be used and in most of the situations the post-mortem examinations are conducted during the day time. If due to unavoidable circumstances, it is to be conducted after sunset. The special orders of the magistrate are to be obtained.
Doors
It should be wide enough to allow for passage of portable X-ray machine. Preferably, it should be sliding door.
Corridors
The corridors should be wide to allow passage of trolleys and X-ray machine, etc.
Lightening
As far as possible there should be adequate day light and in addition to it, there should be provision of the artificial light with stand by generator. Illumination for various rooms of the mortuary is recommended at the following scale.
| SI. No | Rooms | Lumen/sq. feet |
| 1. | Post-mortem room | 25 |
| 2. | Post-mortem table | 150 |
| 3. | Forensic specialist room | 15 |
| 4. | Storage chambers | 10 |
| 5. | Change room | 7-10 |
| 6. | Trolley bay, corridors, stores | 7-10 |
| 7. | Waiting area for relative | 7-10 |
Ventilation
The exhaust fans are required and at least 10 air changes per hour are recommended.
Supply of Hot/ Cold water
Adequate arrangement for provision of heated and cold water should be made.
Drinking water facility
There should be provision of safe drinking water.
Wash Bin
Facilities for hand washing with soap separately for the staff and visitors is required.
Air Conditioning
If resources are available, it is desirable to have AC facilities.
Fire Fighting
Fir detection, fire alarm and fire fighting system must be in place.
The staffing will depend upon the size and type of the hospital. If the hospital is associated with a medical college the staffing requirements would be different. As a general guide two forensic experts for 150 autopsies and one additional expert for every 100 autopsies. In addition to the above, the additional requirement of staff is as follows:
Following types of equipment’s are required in the mortuary of the hospitals:
| SI. No | Name of the equipment | District Headquarters Hospital 301-500 bedded |
| 1. | Mortuary table (Stainless steel) | 2 |
| 2. | P.M. equipment’s (list) | 6 |
| 3. | Weighing machine (organs) | 2 |
| 4. | Measuring glasses (liquids) | 4 |
| 5. | Aprons | 10 |
| 6. | PM gloves (Pairs) | 20 |
| 7. | Rubber sheets | |
| 8. | Lens | 2 |
| 9. | Spot lights | 4 |
The mortuary services are very sensitive services of the hospital at one hand in the sentimental values of relatives are attached with the decreased and other hand the medico-legal importance of the case. The situation is to be handled with great care. There should be a standard operative procedure (SOP) for the important issues like:
a. Daily check
i. Temperature in cold chambers
ii. Compressor check
iii. Check for cleanliness
iv. Gas pressures.
v. Water level.
b. Monthly check
i. Motors
ii. Generators
iii. Wiring of electricity
iv. Embalming machines
c. Half yearly check
i. Preventive maintenance of equipment’s
ii. Change of compressor’s oil
iii. Greasing of motors
d. Record maintenance
e. Work load assessment