For most of the people hospital means the ward. It is in reality also. Basically, people go to hospital for two purposes; either to seek out door consultation in the OPD of the hospital or for admission to hospital and get treatment as inpatient. The consultation can be done in the consulting chambers outside the normal OPD of a hospital also. For hospitalization we necessarily require an Inpatient Department (IPD). The IPD consists of the following components:
The functions of inpatient department are:
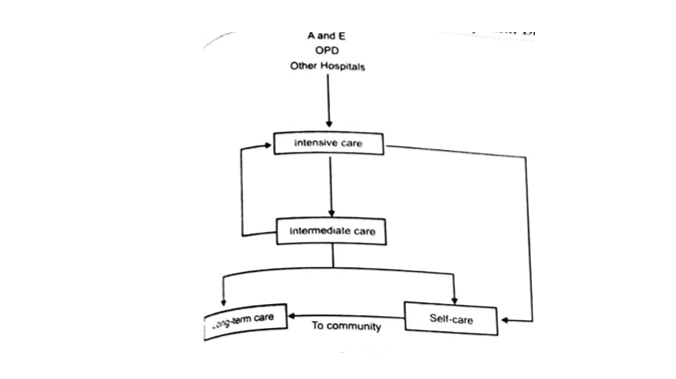
In this system the inpatient area is divided into separate sections. The first section is of intensive care unit, which takes patients in acute stages of illness. The second is the intermediary unit. The third is the convalescent unit, which takes patient who are nearly recovered and need the minimum of care. The argument for this system is that it facilitates the concentration of staff and equipment in the intensive care unit and that it leads to general economy and to better service to the patient.
Factors taken into consideration for planning of Nursing Unit:
The IPD forms 33% to 50% of the structure of the hospital construction and most of the equipment’s and staff are housed in this department or area. Maximum amount of medical care, medical teaching, training and research is concentrated in this department. This is the hospital area, which gives maximum output of services, name and fame to the hospital and of course maximum amount of stress to the staff and so maximum vigilance is required to prevent litigation and patient’s dissatisfaction.
It should be situated away from the main roads and from OPD to avoid disturbances and potential source of cross infection. It should be approachable for supportive services. The intramural transportation should be well planned for effective and efficient transportation of the staff, patients and supplies, with n the hospital.
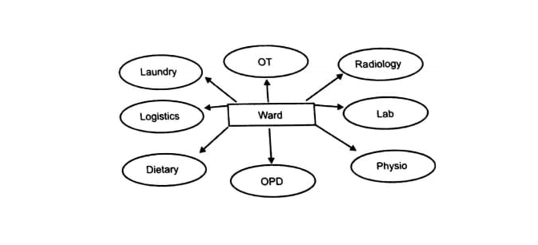
The various departments of the hospital, clinical, diagnostic, therapeutic, utility, support services are interrelated, they have to work in perfect coordination, for effective utilization of the services of the in-patient departments.
There are two types of arrangements in most of the hospitals.
It is common practice to plan IPD accommodation in fairly tall buildings with a central vertical spine, through which run the lifts, conveyor belts and stair cases needed for vertical circulation.
In patient areas horizontally in single or two storey buildings linked by horizontal corridors. This arrangement has got advantages. It facilitates growth and reduces or eliminates the requirement for expensive vertical transportation system, particularly lifts. It is suitable for small size inpatients up to 300 bed strength.
Size of the ward is dependent upon various strength:
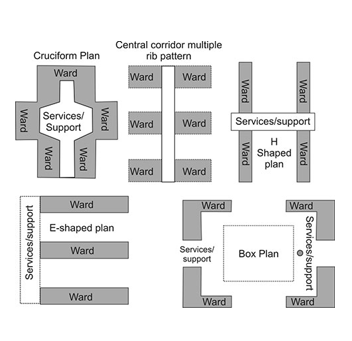
There are various types of ward designs; some of them are being described here.
The rectangular pavilion type of ward was designed in the year 1770 by Frenchman, later it was adopted by Florence Nightingale and is known by her name. The characteristics of the Nightingale ward are:
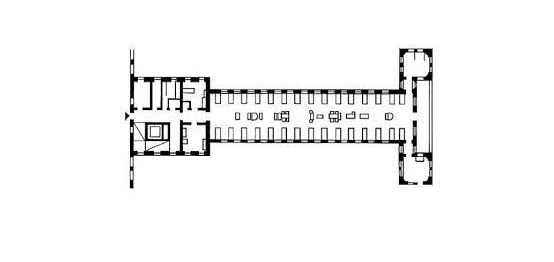
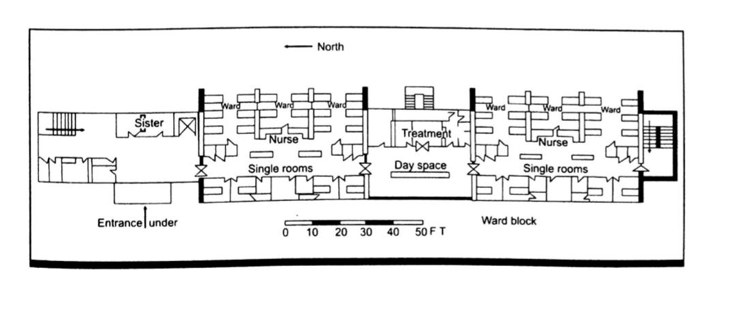
The modified nightingale ward has got the nursing station in the centre of the ward, the ancillary, auxiliary services are provided at one end and the utility services at another end. The nurse’s travel time has been reduced and the supervision over the patient’s condition also improved in the modified pattern of ward.
The ward unit is divided into small compartments or cubicles separated from each other by low partitions. Each cubicle having 1, 2, 4 or 6 beds arranged parallel to the longitudinal walls. In developing countries due to resource crunch, it may not be possible to maintain the wards entirely on Rig’s patter. However, the Committee on Plan Project (COPP) has recommended two single bed rooms in every ward of 20-30 beds, for the patients who require special nursing care.
Advantages
The Advantages are:
Disadvantages
The Disadvantages are:
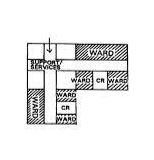
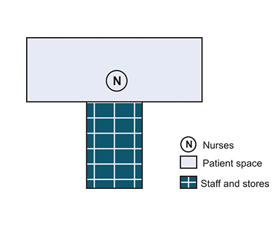
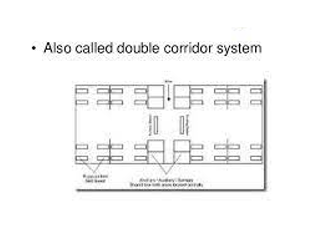
There are four important components of the nursing unit of the hospital:
It consists of single bed room or multiple bed rooms. The size of room required for various types is given as under:
| No of Beds | Recommended Space |
| 1 bed | 14 sq. meter |
| 2 beds | 21 sq. meter |
| 4 beds | 28 sq. meter |
| 6 beds | 42 sq. meter |
The distance between the bed end and the wall is 0.25 m and distance between the two beds is 1.25 m. The distance between the beds should permit hassle free
It consists of the following facilities:
This is the nerve centre of the ward unit and should be so located that the nurses can keep a watch over as many patients as possible. The distance to the farthest patient should not be too much. In the Rigs pattern the acute patient are housed on either side of the nursing station with provision of large glass window for direct observation. The size of nursing station is about 20’ x 20’ with sister’s room, large work table and build in cup board.
It will have following areas:
1. Dirty Utility room
2. Bathroom and WC
a. Urinal: One for 16 beds
b. WC: One for 8 beds
c. Bath room: One for 12 beds
d. Wash basin: One for 10 beds
3. Janitor Room.
1. Water approximately 300 litters. /bed/day round the clock supply.
2. Light:
a. Point should be carefully designed
b. Glare free
c. Natural light should be planned
d. One industry switch for machines like portable X-ray
e. One 15 Amp and one 5 Amp switch in each cubicle
f. Night lamps.
There should be an effective two-way communication, paging system and mobile or cell phone system is the need of the hours. One broad band connection is desirable in each nursing station/ward for easy access of the medical library.
Centralized air conditioning of nursing units helps in patient’s comfort and reduces hospital acquired infections.
It is normally common between 2-3 wards or for each floor. It will include:
1. Ward laboratory
2. Seminar Room
3. Employee’s rest room and changing room
4. Nurse’s rest rooms
5. Visitor’s room
6. Duty Medical Officer’s room, Sister’s room may be provided at the scale of one per floor or for 2 to 3 wards. MG. Trolley Bay on floor basis of 400 beds or above
7. Other facilities like:
a. Cold and Hot Water supply
b. Piped gas for heating
c. Clerical outlet’s purpose
d. Nurse call system, telephone, clocks, etc.
In addition to the wards discussed above there are some special types of wards with specific requirement like:
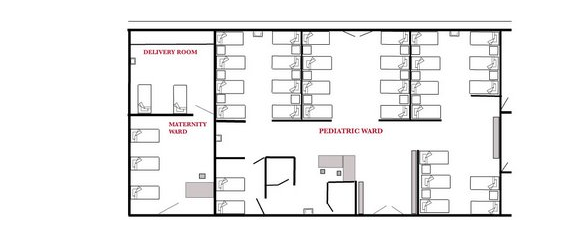
Special consideration for planning for children’s ward include the provision of a large proportion of isolation rooms and facilities for mother to come into the hospital with their children. There is also need of play room.
The maternity ward of the general hospital needs to be linked very closely with clinics or health centres established in the community near the homes. The maternity department of a district hospital should have a separate entrance, as child birth is a physiological and not pathological process, and it is undesirable that a woman should associate a normal function with the care of the sick. The provisions in the maternity wards will depend upon:
The psychiatric ward if possible, should be located on the ground floor. It is desirable to treat the psychiatric department as s separate wing of the hospital, physically linked to it. Many small one bed rooms are desirable; larger bed rooms should be subdivided by means of curtains to give the patients privacy. One or two isolation rooms are adequate for a unit of 24 beds. If possible, a hair dressers and small beauty parlour should be included in the hospital ward design.
1. Medical
| MO | 1 MO/12-15beds |
| General medicine | 1 specialist/100beds + 1 additional/50beds |
| General surgery | 1 specialist/100beds + 1 additional/50beds |
| Gynae & Obstetrics | 1 specialist/100beds + 1 additional/40beds |
| Paediatrician | 1 specialist/100beds + 1 additional/150beds |
| Anaesthesia, Dentistry, Radiodiagnosis, Pathology, Orthopaedics, Ophthalmology, ENT, Skin & VD | 1 specialist/100beds + 1 additional/150beds |
| Psychiatric, biochemistry, microbiology | 1 per hospital above 200 beds |
| Chest disease & TB | 1 per hospital above 200 beds + 1 for additional 200 bed |
| Forensic Medicine | 1 per 1500 bed |
2. Nursing
| Nursing Personnel | Staffing nurse |
| NS | 1/hospital |
| Dy. NS | 1 up to 400 beds + 1 additional/200 beds |
| 1 assistant NS | 1 for 100-150 beds & 3-4 wards |
| Ward sister | 1 for 25-30 beds on one per ward |
| Teaching Hospital | 1 nurse for 3 beds |
| Non – Teaching Hospital | 1 nurse for 5 beds |
| ICU/CCU | 1 nurse for 1 bed (+ 30% on leave reserve) |
| Infection control nurse | 1 nurse/250 beds |
The nurse patient ratio depends upon the:
| Category & nature of illness per patient per day (24hr) | Direct Nurse Hour | Nurse Patient Ratio |
| A. Critically ill patient needing intermediate care | 8-10hrs | 1:1 |
| B. Moderately ill patient needing intermediate care | 3-5hrs | 1:3 (Teaching hospital) |
| 1:5 (non-teaching hospital) | ||
| C. Mildly ill patient needing self-care | 1-2hrs | 1:6 (Teaching hospital) |
| 1:10 (non-teaching hospital) | ||
| D. Chronic ill patient requiring skilled & prolonged nursing care | 30minutes | 1:12 (Teaching hospital) |
| 1 hour | 1:18 (non-teaching hospital) |
| No of Hospital beds | No of Group ‘D’ Staff | Suggested Norms |
| 30-50 | 15-25 | 1 Gr. D/2beds |
| 100 | 50 | -do- |
| 200 | 100 | -do- |
| 300 | 150 | -do- |
| >500 | 250 | -do- |
Management defined in a simple language is to get the work done in a systematic way for accomplishment of defined objectives based on management of Men, Money and Materials, Machines, Methods and Minutes. Management gives us the clue as to how to get best possible services and how to make the ward administration effective and efficient. It is also said that management is a process by which a cooperative group directs action towards common goals. Ward management is facilitated by the development of systematic procedures for dealing with the details of ward functions by adoption of a system of day-to day tasks. The ward management is basically an operational management. The ward management is the key to success of the hospital. The image of a hospital depends to a large extent upon the patient’s satisfaction. The patient’s satisfaction is dependent upon the effective and efficient ward management. The effective ward management depends upon the technical skills and ability of the ward sister. Another important fact about the ward management is, ward is a matrix organization, a very complex organization. It is to be managed on the principles of a project management. The ward sister is under the dual command, at one hand she is under the command of the physician in-charge of the ward/department at other hand she is under the command of nursing superintendent. This makes management of the ward a very challenging job. While managing a ward, the manager has to apply various managerial skills which differ as per the level of the management. The student is advised to consult the introductory chapter on management in the same book. The nurse manager has to apply the whole management process while managing the ward/unit and to follow all the management principles.
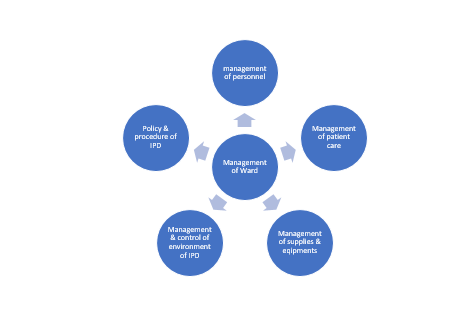
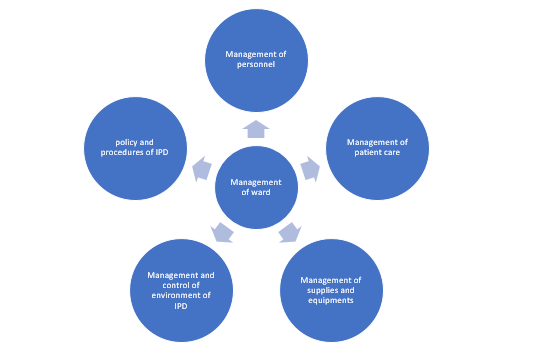
Objectives
The objectives of ward management can be classified as:
Main role in ward management is performed by the nursing unit. This nursing unit forms the system, ensures its proper implementation and performs evaluation towards the care and comforts of the patients with full supervision. A nursing unit should be so designed that it can operate at minimum cost and can at the same time also achieve the functional goals of the ward. The nursing unit has to be an efficient unit of the hospital. Much of the care in the hospital is dependent upon the quality output of the nursing services: The person in-charge of a nursing care in the ward is called ward-sister or sister-in charge.
It is the legal responsibility of the nursing administrator/ward in-charge to provide and ensure quality care to the patients. The administrator/ward in charge should instruct his/her employees to be very cordial and sympathetic with the patients and their attendants besides providing the quality care to the patient. She is the spokes person, she is the leader and responsible for the liaison with the staff, patients, visitors, VIPs, press and everybody coming to the ward. The importance becomes even more in the crisis situation.
Management of personnel is not an easy job. The nursing administrator/ward in-charge has to create a working environment providing facilities and services within the reach of all categories of staff. He/she has to motivate the subordinates to achieve the organizational goals. She has to be communicator, motivator, leader, and counsellor and disturbance handler in the ward; most of the time her presence is felt in the wards. The clinicians come to ward and go back to their respective department, handing over their responsibility of patient’s care to the nurse.
Coordinating is the integrating process in an orderly pattern of group effort; in any hospital toward the accomplishment of a common objective. To ensure the harmonious and smooth working of an organization with a number of its divisions, departments or units, the activities in all areas are required to be pulled together, unified and blended so as to give them a common purpose. Coordination is basically synergy. The diverse departments are brought together to work for a common purpose of rendering quality care to the patients in the wards. Much of the name and fame of the hospital is dependent upon the work of the nurses. Coordination must have time, quantity, and direction dimensions. Coordination is different from cooperation; in cooperation people help each other to accomplish their objectives; in coordination it is the combined and synergistic effort to achieve the common organization objectives. It is a mutually arranged effort of the requisite quality and quantity, arranged at the proper time through deliberate executive action.
Counselling in general is defined as helping people to help themselves. It is the process of helping a person to solve his problem by himself. Counselling is also defined as a conversation between two people for the purpose of solving the problem.
The term strategic management has been borrowed much from the military sciences. It is more appropriate in the war like situations. The strategic management has become very popular in the service industries also. This is basically dependent upon the following factors:
The operational management is basically management on short term and day to day basis at the operational level. Strategic management gives a direction, while operational management works towards this strategy. The objectives should be to provide comforts and good quality care to the patients, as a short term, while long term objective should be improvement and establishment of a system for the functioning of the ward.
Monitoring is the observation and recording of the discrete activities; with a plan. The evaluation is it extent on good monitoring the ward is monitored by various mounds. Nursing is a dynamic, therapeutic and educative process in meeting the health needs. The activities undertaken by the nurses are:
Nursing needs of patient
Functions of the Nursing Care Services of the hospital
1. Patient care: Providing optimum care to the patient. This includes all activities necessary to provide nursing care:
a. Concerned with comfort and well being of every patient.
b. Assessment of patients need and planning of care.
c. Concerned with carrying out of medical treatment. Helping physician in carrying out procedures, preparing equipment for assisting physician with diagnostic tests and therapeutic measures. Giving medicine and carrying out treatment, observing patient for any untoward reaction following treatment and making necessary measures to combat them.
d. Concerned with education of Staff Nurses (incidental and planned).
e. Concerned with patient and relatives about maintaining and improving his health and to carry out his treatment when he goes home.
2. Administration: Through which the unit functions.
3. Education: The organization of education program for nursing students.
4. Housekeeping: Involves in maintenance of clean, safe and comfortable environment. There should be a place for everything, and everything should be in its place.
5. Clerical: Involves maintenance of records and reports.
6. Maintenance of supplies and equipment: Involves timely maintenance of equipment, and maintenance of supplies for carrying out unit activities.
7. Off-station duties: The activities which take nurses away from the unit but have definite relationship to the patient or the unit.
8. Patient care: It is the nucleus of all the activities of the ward, which includes comfort, nutrition, human needs, and special care of the patient. It also includes preparing patient for procedures and follow up there after, carrying technical procedures, health education, supportive care, recording, collection, examination of specimens.
9. Discipline: Nursing unit should be able to maintain discipline in the ward.
Factors Influencing In-patient Care
Factors influencing inpatient care
Medical audit is entirely different from the general perception of the audit, what is in the minds of the people. “Medical audit is the evaluation of medical care in retrospective manner through analyzing the clinical records”. The objective of medical audit is ultimately improvement of patient care. This topic has been discussed in the chapter on quality in health care.
The earliest historical references to organized nursing services are based upon the work of the religious orders-heroic bands of sisters who dedicated their lives to personal and devoted service. Another source of nursing tradition has been the military influence. Tribute must be paid to Florence Nightingale, pioneer in modern nursing and modern hospital administration.
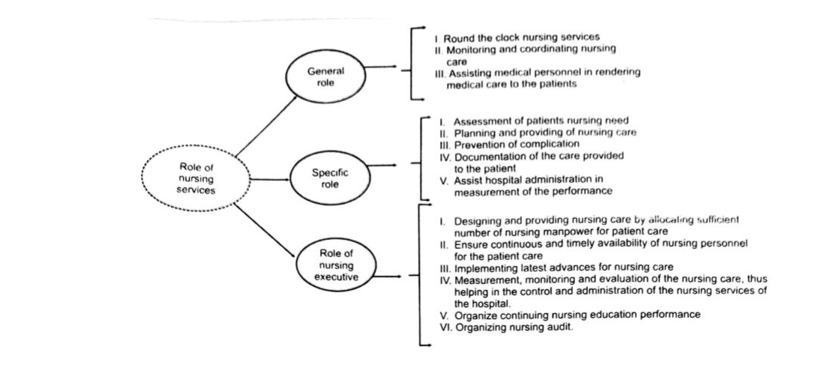
Florence Nightingale was born on 12 May 1820, and named after the city of her birth. Her wealthy parents were in Florence as part of a tour of Europe. In 1837, Nightingale felt that God was calling her to do some work but wasn’t sure what that work should be. She began to develop an interest in nursing, but her parents continued it to be a profession inappropriate to a woman of her class and background, and would not allow her to train as a nurse. They expected her to make a good marriage and live a conventional upper class woman’s life. Nightingale’s parents eventually relented and in 1851, she went to Kaiserwerth in Germany for 3 months nursing training. This enabled her to become superintendent of a hospital for gentlewomen in Harley Street, in 1853. The following year, the Crimean War began and soon reports in the newspapers were describing the desperate lack of proper: medical facilities for wounded British soldiers at the front. Sidney Herbert, the war minister, already knew Nightingale, and asked her to oversee a team of nurses in the military hospitals in Turkey. In November 1854, she arrived in Scutari in Turkey. With her nurses, she greatly improved the conditions and substantially reduced the mortality rate. Florence Nightingale earned the nickname “The Lady with the Lamp” for her tireless nursing of British soldiers during the Crimean War. She returned to England in 1856. In 1860 she established the Nightingale Training School for nurses at St Thomas’ Hospital in London. Once the nurses were trained, they were sent to hospitals all over Britain, where they introduced the ideas, they had learnt, and established nursing training on the Nightingale model. Nightingale’s theories, published in ‘Notes on Nursing’ (1860), were hugely influential and her concerns for sanitation, military health and hospital planning established practices which are still in existence today. Her outspoken Notes on Matters Affecting the Health, Efficiency and Hospital Administration of the British Army (1857) and Notes on Hospitals (1859) helped create changes in hygiene and overall treatment of patients. She also founded the ground-breaking Nightingale Training School for nurses, and in later years published dozens of books and pamphlets on public health. Nightingale was awarded the Royal Red Cross by Queen Victoria in 1883, and in 1907 became the first woman to receive the Order of Merit. She died on 13 August 1910. Florence Nightingale is rightly called the father of Hospital Administration. In India, notable among these are Charaka Samhita, Ashtanga Hridaya and the writing of Sushrata. Emperor Asoka built many hospitals and employed nurses. As per their writings, the nurses of those days should be proficient in cooking, in caring for bed patients and in other nursing procedures. Perhaps nursing schools existed even in those days. Organized training for nurses in India can be said to have started in 1854 with the opening of a school for midwives at Madras. Soon schools for nurses training were opened in Calcutta (1859) and in Madras (1871). To cater for the demands of the Army during World War, Lady Reading Health School was opened in Delhi in 1918 to train nurses. Training of male nurses was also started during the early period of this century The next important step in the development of nursing was the formation of Trained Nurses Association in 1908 and passing of Nurses Registration Act, in Madras in 1926. Soon various provinces except Assam formed Provincial Nursing Councils by 1939. After the Bhore Committee’s recommendations in 1946, the Indian Nursing Council was formed in 1949. Today the nursing has grown into a full-fledged profession; some schools have also started teaching programs in super specialty nursing. The National Health Policy 2002 has also envisaged the importance of development of courses in super-specialty nursing. Functions of nursing services broadly imply planning, leadership, coordination and control over all responsibilities as regards to the provision of nursing care, in terms of quality, quantity efficiency and effectiveness.
Functions of Nursing Services
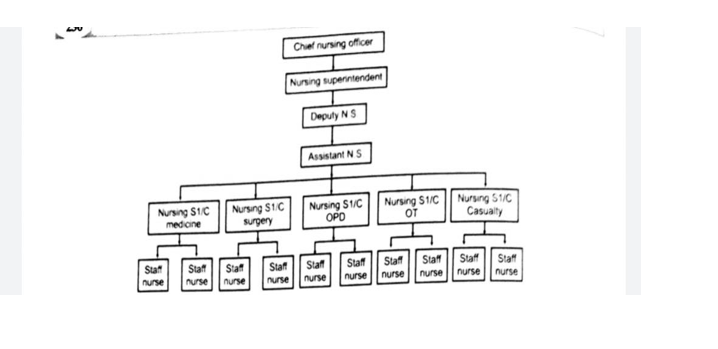
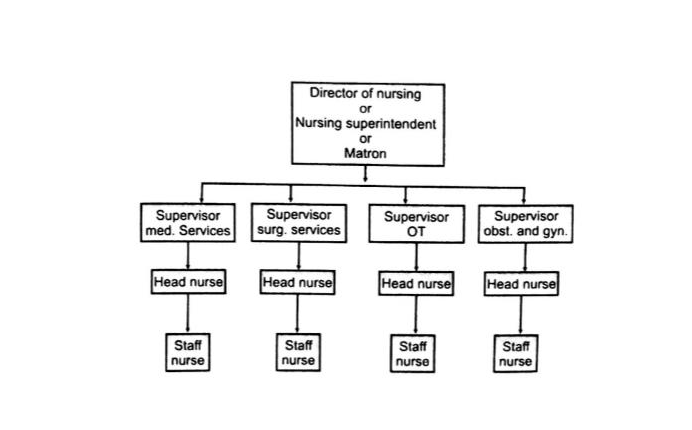
The typical organization of the nursing services of a general hospital is given as under:
It can be seen from above chart, that the work of the various nursing units, nursing services is coordinated by a superior and the general coordination is affected by the nursing superintendent, through her juniors. In case of a teaching hospital, there may be chief instructor who may be functioning under the Nursing Superintendent.
Qualifications
Master in Nursing (with any specialty) with 6 years experience of which 3 years in administration.
Or
Post Basic BSc. Nursing with 3 years’ experience in any position.
Or
Basic B.Sc. Nursing with 10 years total professional experience.
RN, RM with Diploma in Hospital Administration preferable with 10 years experience in administration.
The Nursing Superintendent is responsible to the Medical Superintendent. The Deputy Nursing Superintendent (in hospitals with less than 150 beds) is reporting to the Medical Superintendent. In hospitals where the post of Nursing Superintendent exists, the Deputy Nursing Superintendent will be reporting to the Nursing Superintendent.
Where the post of Nursing Superintendent and Deputy Nursing Superintendent both are existing the two share the following duties and responsibilities. Where no post of Nursing Superintendent is in existence, the Deputy Nursing Superintendent carries out the duties and responsibilities along with the Asst. Nursing Superintendent.
Qualification
RNRM/B.Sc. Nursing with 5 years experience as Ward In-charge.
Line Authority
The Assistant Nursing Superintendent is directly responsible to the Deputy Nursing Superintendent and the Nursing Superintendent. In hospitals where the Assistant. Nursing Superintendent is the only post then, she is directly reporting to the Medical Superintendent.
Duties and Responsibilities
Job Title: Sister
Place of Work: Hospital
Class/Level: Gazetted 3rd Class
Qualifications: RN/RM/BSc in Nursing
Experiences: According to Civil service
Responsible For: Staff Nurse, ANM and Supporting staff.
Responsible To: Matron, Assistant Matron, Hospital Director, various departments of hospital and other national and international agencies.
She plays role of manager in unit where there are above 25 beds and as nursing administrator in 25 bedded hospitals. She also plays a role as educator, supervisor, researcher, facilitator, counsellor and evaluator within her department.
1. Assesses the situation of given unit in relation to different types of patient’s care, facilities provided by the nursing personnel.
a. Functions of ward-sister
i. Quality care of the patient
ii. To carry out instructions given by the doctor
iii. Guides and supervises the staff under her control
iv. Proper orientation of the ward staff
v. Evaluation of performance of ward staff on a regular basis through systematic and scientific methods
vi. Proper management of ward
vii. Housekeeping services in the ward
viii. Infection control practices in the ward I in particular reference to the biomedical waste disposal
ix. Occupational safety of the nursing and other category of staff of the ward
x. Identifies the patient’s need/problem in the unit.
xi. Assigns the patient’s care and others activities to nursing personnel.
xii. Evaluates the patient’s care given by nurses.
xiii. Attends doctor’s round and Matron and Assistant Matron’s Clinical rounds.
xiv. Checks and caries out and delegates doctor’s instruction and order after round.
xv. Participates and refers the patient for rehabilitation therapy. Vin. Guides and conducts health education activities.
xvi. To patients as required including MCH/FP, disease, control and health promotion.
b. Supervisory Activities
i. Guides and supervises all staff for giving bed side nursing care.
ii. Maintains regular records, report concerning the patient’s care.
iii. Provides direct guidance and supervision of nursing and non-nursing personnel for the efficient running of the wards and in carrying out nursing routines, bearing in mind the individual needs of patients.
iv. Encourages, motivates, assesses the effectiveness of their own works and develop their potential for giving good nursing care.
v. Uses the standard guideline and manual for supervision.
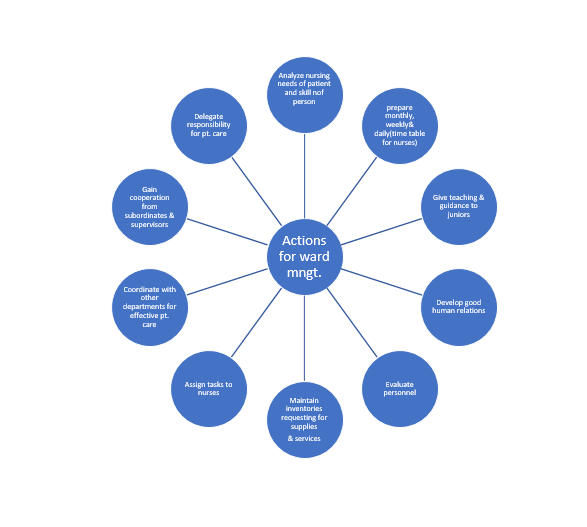
c. Administrative Activities
i. Makes duty roaster for 24 hrs coverage in unit of the Hospital.
ii. Conducts nursing conference, meeting and individual conference when necessary.
iii. Investigates complaints promptly and takes action according to rules and policy of the hospital.
iv. Reports and records absence and sickness of staff including leaves.
v. Maintains cleanliness of the ward and its environment, furniture, equipment, ventilation, lighting, heating, noise, odours.
vi. Maintains adequate linen, other supplies, requisition for ward stores and repairs, replaces supplies as necessary.
vii. Keeps up to date record of drugs and maintains records of its administration.
viii. Checks and manages all equipment’s periodically, to see that it is in order.
ix. Checks daily availability and conditions of emergency equipment’s and supplies.
x. Maintains inventories, reports, breakages and losses.
xi. Helps in controlling the visitors of patients as necessary.
xii. Ensures that relatives of very ill patients are allowed to stay with patients when necessary.
xiii. Accompanies, the Matron on the round and reports to her any important incidents.
xiv. Informs Matron immediately of any special emergencies or accidents in the ward, and keeps a written record of any incidents.
xv. Coordinates between Matron and staff in her unit and also with other departments.
xvi. Takes active part in condemnation of useless materials.
xvii. Helps Matron for annual plans and budgets in her ward.
xviii. Delegates responsibilities to the responsible person in her absence.
xix. Assists the Matron and Assistant Matron for disaster plan and organization.
d. Educative Activities
i. Identifies the learning need of staff in ward.
ii. Plans, conducts and recommends the in-service education and training program for her staff.
iii. Manages and facilitates the clinical teaching activities for the students and staffs.
Qualification
General Nursing and Midwifery (alternative courses for Male students) or the new general program. Nursing from a recognized university.
Job Specification
The Staff nurse is the second in nursing hierarchy in the ward. She works under the ward-in-chief. Her duties and responsibilities can be divided as under:
Administrative
Nursing Care
| A | Labour room | Difficult & abnormal deliveries. Premature baby care. |
| B | OT | Care of instruments & gloves. |
| C | Mental Hospital | Prepare patient for ECT & assist doctors care of mentally retarded (where such a unit exists) |
| d | ICCU | Total patients care, helping with ECG or any other investigative procedure. |
Teaching
Staffing is the important managerial function. Staffing involves the selection of personnel and assignment systems and the determination of staffing schedules. There are many variables to be considered when planning for staffing. The nursing care of patients in hospital depends on the numbers and quality of nursing personnel. The number of nurses required to man the nursing services in a hospital, depends on many factors, some of them are:
a. Automation
b. Mechanization
Extensive research has been done to ascertain the average number of hours a patient needs nursing care in a hospital. It has been worked out that average number of bedside nursing hours required per patient in 24 hours is as under:
Every hospital has to work out its own need, based on the above factors. According to the recommendation of the Nursing Committee set up by Ministry of Health. Government of India (Shetty Committee), the ratio of nurses to patients in a hospital should be 1:3 in hospitals where nursing training is imparted other hospitals should have a ratio of 1:5.
It is based upon finding out the needs of patients and availability of personnel. It should result in a sound, realistic, reasonable and understandable plan. Based upon the studies in some general hospital, however, indicate that the effective ratio for their particular need is one professional nurse to two auxiliary nurses.
Shortage of nurse is an old problem existing all over the world. This is partly due to the rapid expansion of medical care programs and the general lack of understanding on the part of the public about the duties and responsibilities of the nurses. The reason for shortage of the nursing manpower in world over is because of various factors, some of the factors have been identified as below:
Ward management and nursing care is considered a scientific profession which is an important part total hospital management and it is very much desired for the care providing at the level of high technological areas of the hospital.
Nursing as per the WHO definition is the part of total health organization which is to satisfy the nursing needs of the community, organization of nursing service is a complete process which helps the institution to stand on its own. Nursing care is “defined as the care of the patient with the specific regard to nursing”.
The nursing services must be under the direction of competent leader, i.e. Chief Nurse Officer/Director of Nursing Service/Nursing Superintendent, who is responsible to the hospital administration for the program and activities of the nursing care of the patient. The Chief Nursing Officer/Nursing Director/ Nursing Superintendent has dual responsibility. The Nursing administrator has to perform dual responsibility in the hospital, the responsibility of nursing administration and coordinating with the faculty for medical care of the patients. Thus, she has entire responsibility of the nursing care and also of the patient care services. In the present scenario when the Government of India is also committed to the improvement in the nursing services as envisaged in the national health Policy 2002, by strongly recommending for the super specialty in the nursing subjects. The nursing services rightly deserve to have a separate department of nursing services in every hospital of large size.
Sanitation and provision of therapeutic environment includes:
There are many methods that may be applied for providing the care to the patient in the ward, but mainly three methods which are practiced for an effective ward management. The tasks of the ward are carried out mainly by these three accepted patterns of Assignments/ methods which depend on the training, experiences and the rules of a particular hospital/institution.
In this method the tasks are divided among the staff, e.g., in a ward one sister (nurse) is made responsible for giving injections, another sister takes care of oral medications and the third sister does all the other works for the patients. In this a nurse is assigned to specific function in the ward as mentioned above, giving injection, oral medicines, taking vital signs of the patients, sponging, bed making, doing any other work of the patient etc. This method is also called efficiency method.
Advantages of the method:
Disadvantages of the method:
In this assignment a nurse is expected to give complete nursing care to one patient. Each nurse is assigned to one or two cases and she is fully responsible for total care of those patients.
Advantages
Disadvantages
It is a new method of assignment/patient care. In this method, the nursing staffs are divided into teams, each of which is led by an experienced nurse. There is one experienced professional nurse, who is being designated as team leader. This leader assigns duties to other nursing staff members of her team for giving care to a group of patients. The team method is very scientific method and is dependent upon the phenomenon of total efforts of all members (TEAM).
Advantages
Disadvantages
Policy
Every hospital must have definite policy, though the basic policy of the hospital is to provide adequate patient care, with available resources. However, certain policies differ from hospital to hospital. Policies govern the functioning of the hospital. The policy is nothing but the broad guide lines issued by the governing board to the different levels of management for day-to-day decision making for smooth administration. Various committees or sub committees are formed to form the policies and check the implementation of these policies.
Procedures
With in the broader framework of the hospital policy, various procedures are followed in providing in patient care. When the patient requires admission, it is given through out-patient department or casualty/ emergency services. Once the patient is admitted, he has to make an Admission Card at the Central Registration Counter on admission. All the records. Of in-patient are written day to day by the authorized hospital staff. All the drugs given to the patient are entered and investigations performed are recorded in a prescribed manner. If any operative procedure is to be performed, then pre anaesthesia check-up (PAC) is to be done and based upon the PAC the operations are performed, after performing the operations, proper operation notes are documented. At the time of discharge, a discharge card is prepared and issued to the patient. The case sheet along with all the records is kept in the Medical Records Department. In the event of death of the patient, a death summary is written and kept for the records, while a death certificate is given to the patient’s relatives. Procedures are step by step approach of doing something or clarity.
Managerial Issues
Management of inpatient services is normally at the following levels:
Nursing Audit
Nursing audit is a new subject in the nursing services which plays a crucial role in the modern era. It may be a good start for improvement of nursing services implementing nursing audit in India, though it has already been started in western countries and found very useful. This is an era of quality management and the nursing audit will definitely help to achieve the quality goals of any hospital.
Nursing audit is defined as “periodic evaluation of nursing service”. Some of the factors evaluated in India are bases for the evaluation, is the qualification and the practical skills of the nursing personnel, turnover of the patients and their satisfaction, correctness and the promptness of the execution of doctor’s orders, dietician’s instructions, pharmacy, sanitation and the cleanliness of the ward. The work which is not inspected is not done is an old saying. Though it used to be relevant in bureaucracy, but it is equally relevant in nursing care also. A periodical review of the nursing care by nursing professional has now become reality. The objective of such type of audits is to improve the services; it is never punitive in nature. Monthly meetings are held to audit a random selection of charts on patient discharged during the preceding month. Now, it has become a felt need of every hospital administrator to implement the nursing audit in the hospital. There can be mainly two types of nursing audits, retrospective and introspective. Audit can be done during the patient’s stay in the hospital or after the discharge from the hospital, depending upon the policy of the hospital. Nursing Audit helps in evaluation of nursing service.
The nursing is a full-fledged profession like the medical. The progress made in the medical field is much more than the nursing profession. There is lot of scope for improvement in the nursing as a profession. Though the nursing profession has contributed significantly in the hospital administration as a specialty, in return the hospital administration has not reciprocated for the all-round growth of the nursing as a profession. The need of the hour is to amalgamate the hospital administration and nursing administration for effective management of the wards or In Patient Department (IPD) of the hospital.